The history of radiation units ties closely to the development of our understanding about radiation and its effects. The discovery of x-rays and radioactivity in the late 19th century by scientists like Wilhelm Roentgen, Henri Becquerel, and Pierre Curie paved the way for the exploration of radiation measurement.
As our knowledge of radiation’s effects on living organisms grew, the need for standardized units became evident. The roentgen was one of the earliest units to measure ionization, followed by the introduction of the curie to measure radioactivity. Over time, advancements in our understanding of radiation’s biological effects led to the development of units like the rem and the sievert.
Creating Radiation Units
The development of the SI system (International System of Units) established a standardized set of units to provide a coherent and universal way to measure radiation. The gray and the sievert were introduced as the primary units for absorbed dose and equivalent dose, respectively, within the SI system.
Four distinct yet interconnected units quantify radioactivity, exposure, absorbed dose, and dose equivalent. The mnemonic R-E-A-D creates a simple way to recall these units, which consist of a combination of commonly used (British, e.g., Ci) and internationally recognized (metric, e.g., Bq) units.1 Below, we will detail the mnemonic and discuss the history of the radiation units along with their relevant scientists:
Radioactivity defines the release of ionizing radiation from a substance. Whether it emits alpha or beta particles, gamma rays, x-rays, or neutrons, the radioactivity of a material is a measure of how many atoms within it decay over a specific period of time. The curie (Ci) and becquerel (Bq) units quantify radioactivity.1
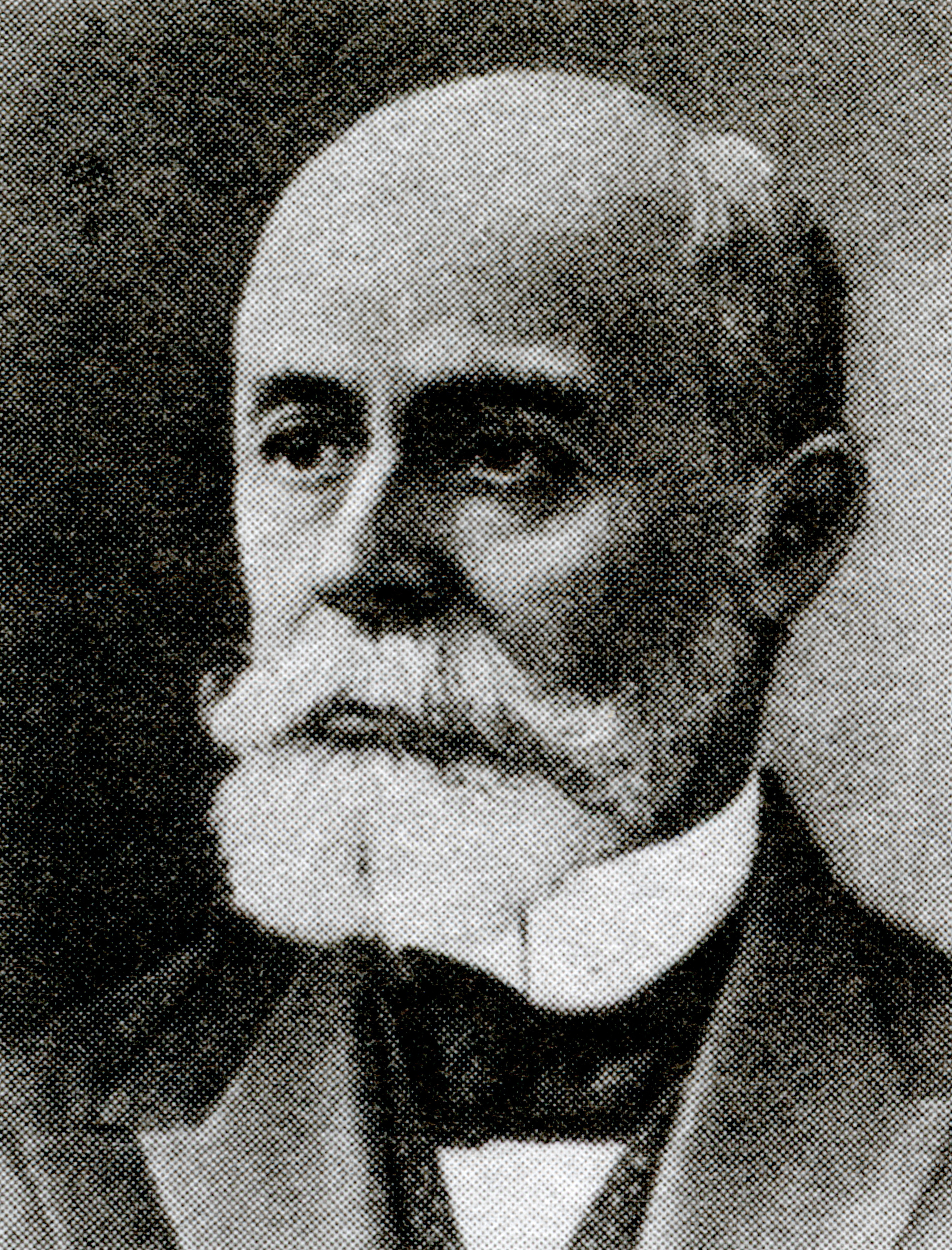
Antoine Henri Becquerel was a French physicist, engineer, and Nobel laureate who discovered evidence of radioactivity. Becquerel’s earliest works centered on the subject of his doctoral thesis: the plane polarization of light, with the phenomenon of phosphorescence and absorption of light by crystals. Early in his career, Becquerel also studied the Earth’s magnetic fields. In 1896, Becquerel discovered evidence of radioactivity while investigating phosphorescent materials such as some uranium salts. For his work in this field, he shared the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics with Marie Curie and Pierre Curie. The SI unit for radioactivity, becquerel (Bq), is named after him.2
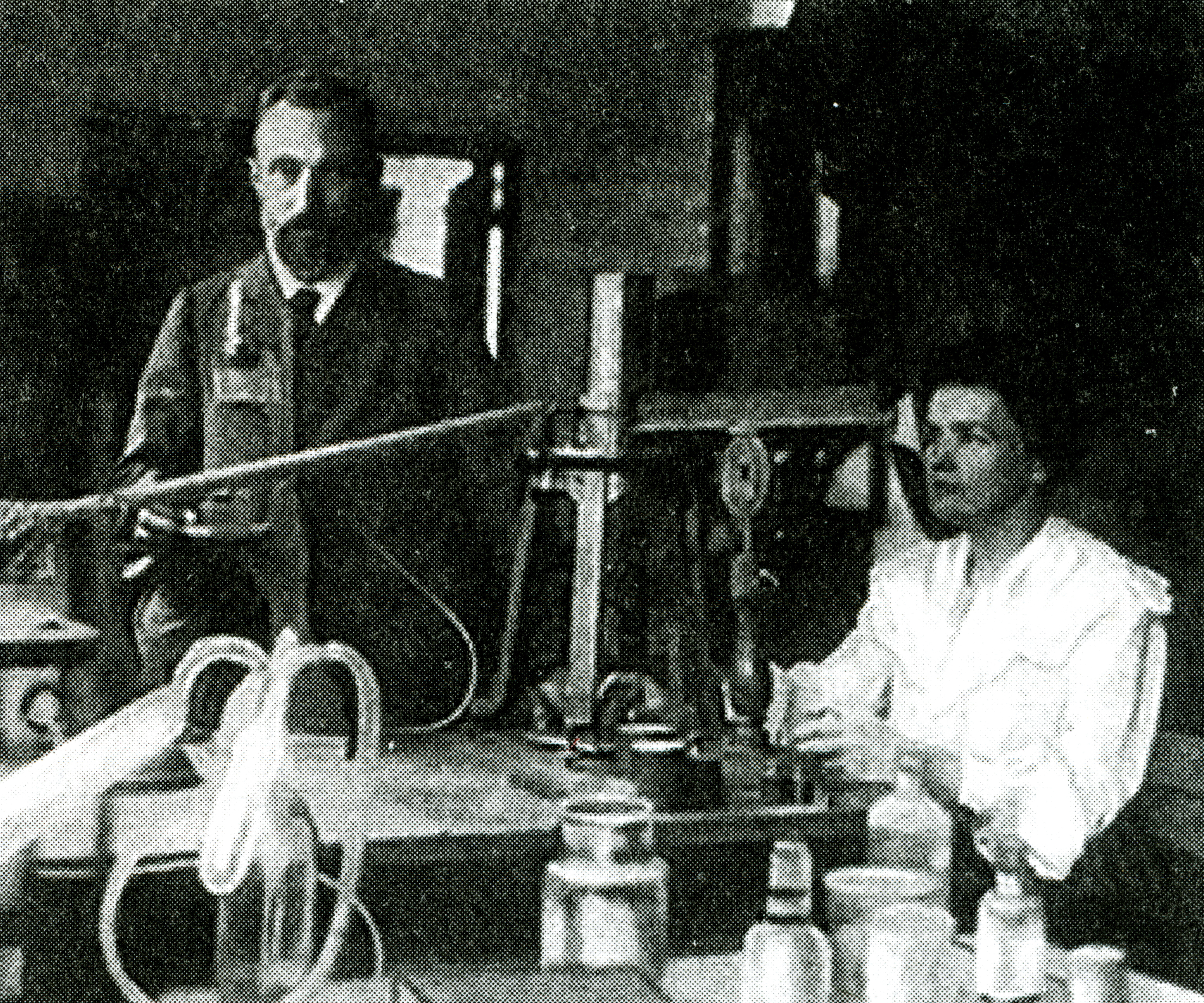
The curie (Ci) unit was created in 1910 by the International Congress of Radiology to measure radioactivity. Pierre Curie, another French physicist, and his wife Marie Curie, who also sat on the committee that named the unit, were the inspirations for the name through their radioactive studies. The original definition of the curie was “the quantity or mass of radium emanation in equilibrium with one gram of radium (element)”.3 In 1975, the becquerel replaced the curie as the official radiation unit in the International System of Units (SI) where 1 Bq = 1 nuclear decay/second4. The relationship between the two units is 1 Ci = 37 GBq (giga becquerels).
Exposure quantifies the extent of radiation going through the atmosphere that reaches a person’s body or a material. Numerous radiation monitors gauge exposure, utilizing the units of roentgen (R) or coulomb/kilogram (C/kg).1

The roentgen is a legacy unit of measurement for the exposure of X-rays and gamma rays. This unit is defined as the electric charge freed by such radiation in a specified volume of air divided by the mass of that air and has the value 2.58 x 10-4 C/(kg air).5 It was named after Wilhelm Roentgen, a German physicist who discovered X-rays and was awarded the first Nobel Prize in Physics for the discovery.
In 1928, the roentgen became the first international measurement quantity for ionizing radiation defined for radiation protection. This is because it was, at the time, the most easily replicated method of measuring air ionization by using ion chambers.6 However, although this was a major step forward in standardizing radiation measurement, the roentgen had a disadvantage: it was only a measure of air ionization rather than a direct measure of radiation absorption in other materials, such as different forms of human tissue. As a result, it did not take into account the type of radiation or the biological effects of the different types of radiation on biological tissue. Consequently, new radiometric units for radiation protection came to be which took these concerns into account.7
The SI unit for measuring exposure to ionizing radiation is coulomb per kilogram (C/kg). Interestingly, unlike other SI radiation units, this unit does not have a specific name. It officially replaced the previous unit, the roentgen, in 1975, with a transition period of at least ten years.8 The SI unit of electric charge, the coulomb, was named in honor of Charles-Augustin de Coulomb in 1880. Charles-Augustin de Coulomb was a French physicist whose best-known work is his formulation of Coulomb’s law. This law states that the force between two electrical charges is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. He also made important contributions to the fields of electricity, magnetism, applied mechanics, friction studies, and torsion.9
Absorbed dose refers to the quantity of energy that is absorbed by an object or person where the energy is deposited by ionizing radiation as it passes through materials or the body. The units, radiation absorbed dose (rad) and gray (Gy), measure absorbed dose.1

In 1953, the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) adopted the unit rad at the Seventh International Congress of Radiology. This was the unit that replaced the rep, roentgen equivalent physical (detailed later in this blog). Although many believe that the rad is an abbreviation of “radiation absorbed dose”, the ICRU never identified it as such. This suggests that the term “rad” was as a standalone word to be a unit for absorbed dose. There was no documented discussion regarding the use of the rad prior to the Seventh International Congress of Radiology. The closest discussion was during the meeting in 1951 when they determined the need for this type of unit. In 1975, the gray (Gy) replaced the rad as the SI unit of absorbed dose where 1 Gy = 100 rad.10
Louis Harold Gray was a 20th century English physicist who worked mainly on the effects of radiation on biological systems. He was one of the earliest contributors to the field of radiobiology. He worked as a hospital physicist at Mount Vernon Hospital in London and developed the Bragg–Gray equation in collaboration with the father and son team of William Henry Bragg and William Lawrence Bragg. Bragg-Gray theory is the basis for the cavity ionization method of measuring energy absorption by materials exposed to ionizing radiation. Gray’s contributions to radiobiology were numerous. Amongst many other achievements, he developed the concept of RBE (Relative Biological Effectiveness) of doses of neutrons and initiated research into cells in hypoxic tumors and hyperbaric oxygen.11 Gray defined a unit of radiation dosage (absorbed dose) which was later named after him as an SI unit, the gray.
Dose equivalent, also known as effective dose, is a measurement that combines the amount of radiation absorbed and the impact it has on the human body. When it comes to beta and gamma radiation, the dose equivalent is equal to the absorbed dose. However, for alpha and neutron radiation, the dose equivalent surpasses the absorbed dose because these types of radiation have a greater biological impact resulting from their increased ability to damage tissue. To quantify dose equivalent, we use the units of roentgen equivalent man (rem) and sievert (Sv).1
Roentgen equivalent man, or “rem”, was first proposed for use in 1945, but under a different abbreviation. The roentgen was the only unit capable of expressing a radiation exposure at the time. However, it fell short being specifically measurable for photons. Workers came into contact with many other forms of radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons, so Herbert Parker, British-American physicist, created units that would be able to gauge exposures to many types of radiation. These were the roentgen equivalent physical (rep) and the roentgen equivalent biological (reb). Due to similarity in pronunciation between rep and reb, reb was eventually renamed to roentgen equivalent man or mammal (rem) to avoid confusion.
The first appearances of the rem unit in scientific literature were not until 1950.10 The rem related to the rad by multiplying the latter by a quality factor (QF) used to account for the varying biological effects of the different types of radiation. The rad in turn may be obtained from the roentgen by multiplying a dose conversion factor. In air, the dose conversion factor relationship between rad and roentgen is 1 R = 0.88 rad. The absorbed dose to a material is in turn found by multiplying 0.88 by the ratio of the mass energy absorption of the material to that of air.12

Rolf Maximilian Sievert was a Swedish medical physicist. He is best known for his work on the biological effects of ionizing radiation and his pioneering role in the measurement of doses of radiation, especially in its use in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.13 Sievert contributed significantly to medical physics, earning him the title of “Father of Radiation Protection”. The sievert (Sv), the SI unit representing the stochastic health risk of ionizing radiation, is named after him. The sievert officially replaced the rem as the international SI unit in 1979 with 1 Sv = 100 rem.14
Conclusion
In summary, the history of radiation units is a journey that reflects the progress in our understanding of radiation’s properties and its impact on living organisms. The development of these units has enabled safer and more accurate measurement and assessment of radiation exposure and its effects on human health. By understanding the intricate relationship between radiation and our bodies, we can now take proactive measures to mitigate its harmful effects and promote a safer environment for all.
Sources
- NRC: Measuring Radiation. Nrc.gov. Published 2017. https://www.nrc.gov/about-nrc/radiation/health-effects/measuring-radiation.html
- The Nobel Prize. The Nobel Prize in Physics 1903. NobelPrize.org. Published 2019. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/physics/1903/becquerel/biographical/
- Curie – Unit of Radioactivity | nuclear-power.com. Nuclear Power. https://www.nuclear-power.com/nuclear-engineering/radiation-protection/units-of-radioactivity/curie-unit-of-radioactivity/
- Bell DJ. Becquerel (SI unit) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Radiopaedia. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/becquerel-si-unit
- Bashir U. Roentgen (unit) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Radiopaedia. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/roentgen-unit?lang=us
- Roentgen – Unit of Exposure | nuclear-power.com. Nuclear Power. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://www.nuclear-power.com/nuclear-engineering/radiation-protection/radiation-exposure/roentgen-unit-of-exposure/
- Roentgen (unit) explained. everything.explained.today. Accessed August 29, 2023. http://everything.explained.today/Roentgen_(unit)/
- Bell DJ. Coulomb per kilogram | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Radiopaedia. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/coulomb-per-kilogram
- Laboratory NHMF. Charles-Augustin de Coulomb – Magnet Academy. nationalmaglab.org. https://nationalmaglab.org/magnet-academy/history-of-electricity-magnetism/pioneers/charles-augustin-de-coulomb/
- Why Did They Call It That? The Origin of Selected Radiological and Nuclear Terms. Museum of Radiation and Radioactivity. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://orau.org/health-physics-museum/articles/selected-radiological-nuclear-terms.html#rad
- LH Gray Memorial Trust: About L.H. Gray. www.lhgraytrust.org. Accessed August 29, 2023. http://www.lhgraytrust.org/lhgraybiography.html
- Dosimetric Quantities and Units. U.S. NRC. Published October 25, 2010. Accessed September 11, 2023. https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ML1122/ML11229A688.pdf
- Aip.org. Published 2023. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://pubs.aip.org/physicstoday/Online/8433/Rolf-Sievert
- Bell DJ. Sievert (SI unit) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. Radiopaedia. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/sievert-si-unit?lang=us